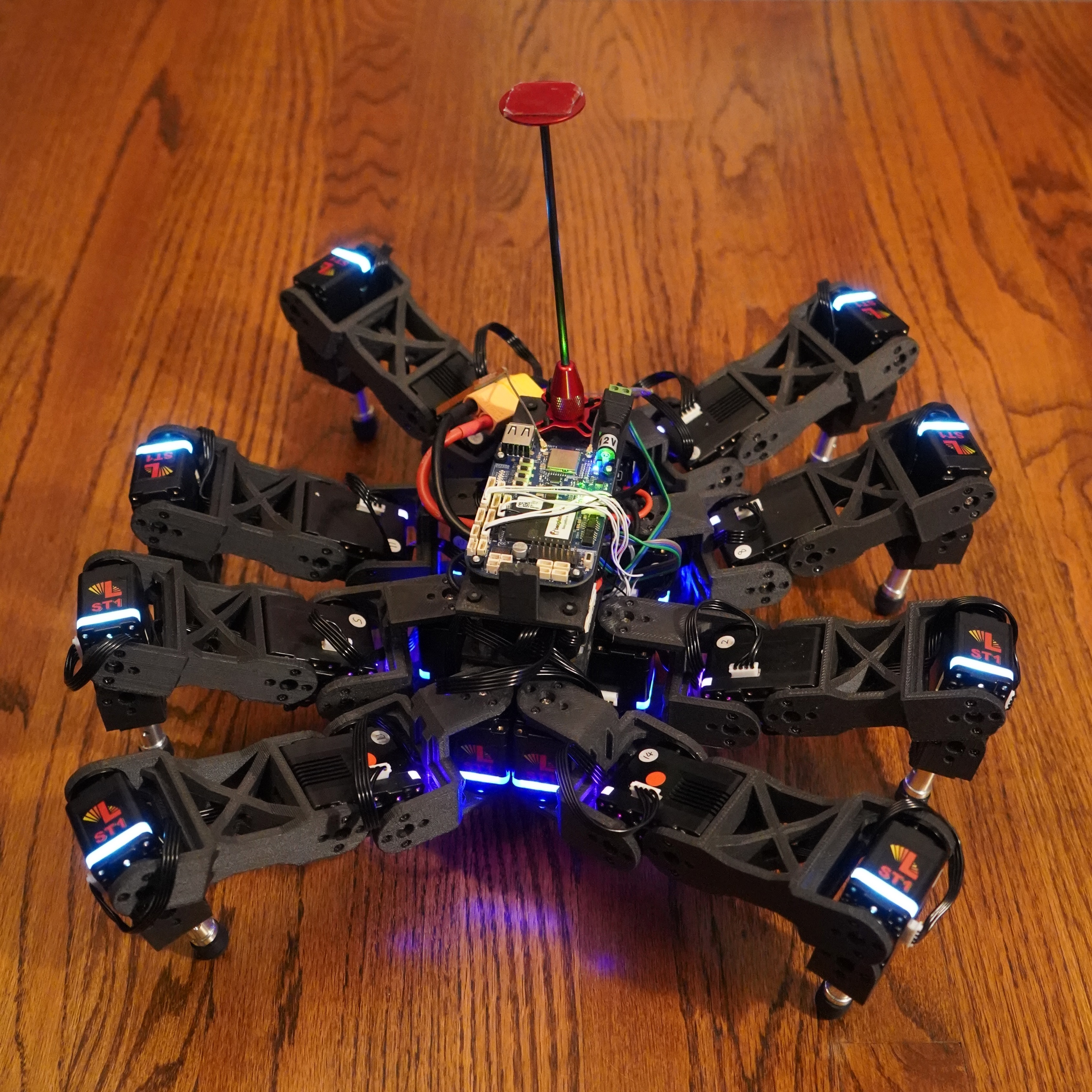
Spidy - Arduino Octopod Robot
Arduino-based 8-legged spider robot with custom radio controller. Features smooth servo motion algorithms, wireless control capabilities, touch-detecting legs, and bionic spider-like movement patterns.
Overview
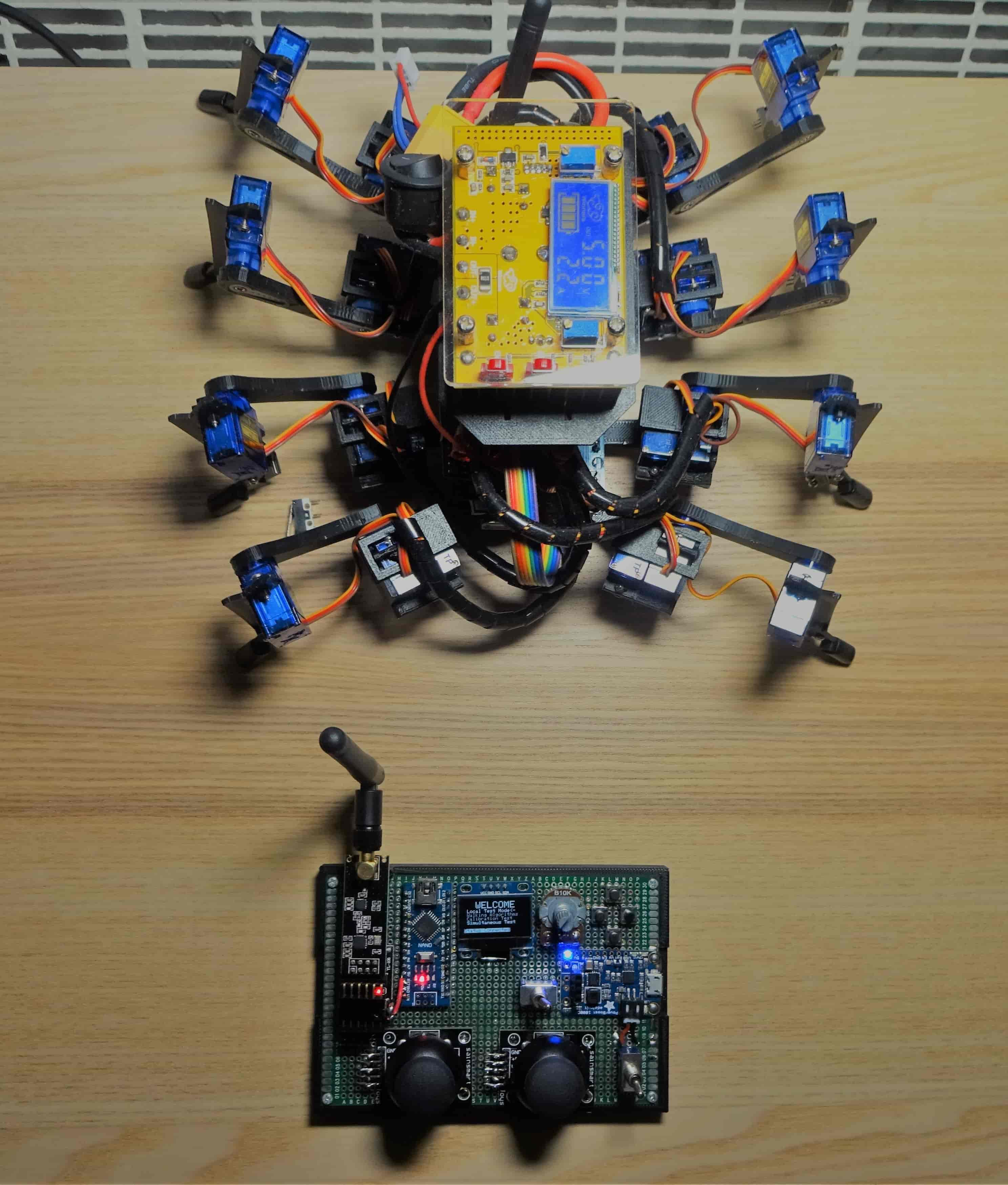
Spidy is an 8-legged spider robot controlled by a custom wireless radio controller. Building this meant solving a fundamental robotics problem: how do you calculate the exact angles for 24 servos to make 8 legs move in coordinated walking patterns? The project explores inverse kinematics, walking gaits, and real-time motion control—all running on an Arduino Mega. View source code and 3D models at the end
The Inverse Kinematics Challenge
The core problem was inverse kinematics—given a desired foot position, calculate the three joint angles needed to get there. Each leg has segments of 44.85mm, 64.5mm, and 12mm. After working through the geometry, I realized I could treat it as solving triangles: calculate the base rotation angle using atan2, then apply the law of cosines to find the other two joint angles.
The breakthrough came from understanding that the middle and end segments form a triangle with the target position. The law of cosines gives you the angles between segments, and you can work backwards from there. Getting this wrong meant legs swinging wildly in the wrong direction—which happened many times before the math clicked. Once the IK worked for one leg, I could replicate it across all eight with different orientations.
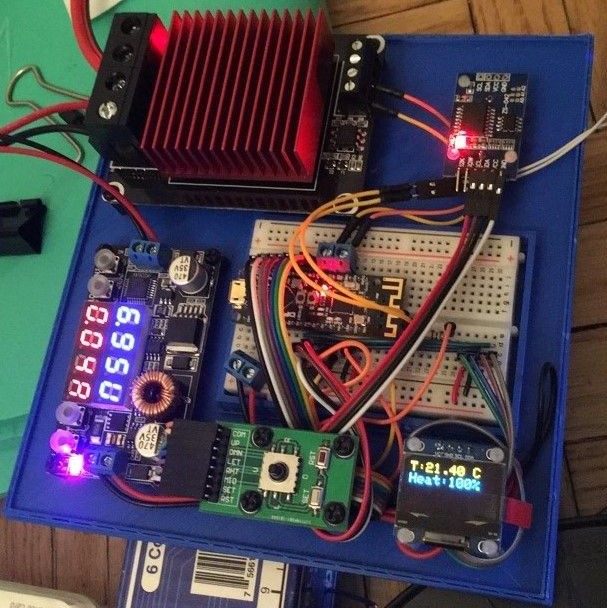
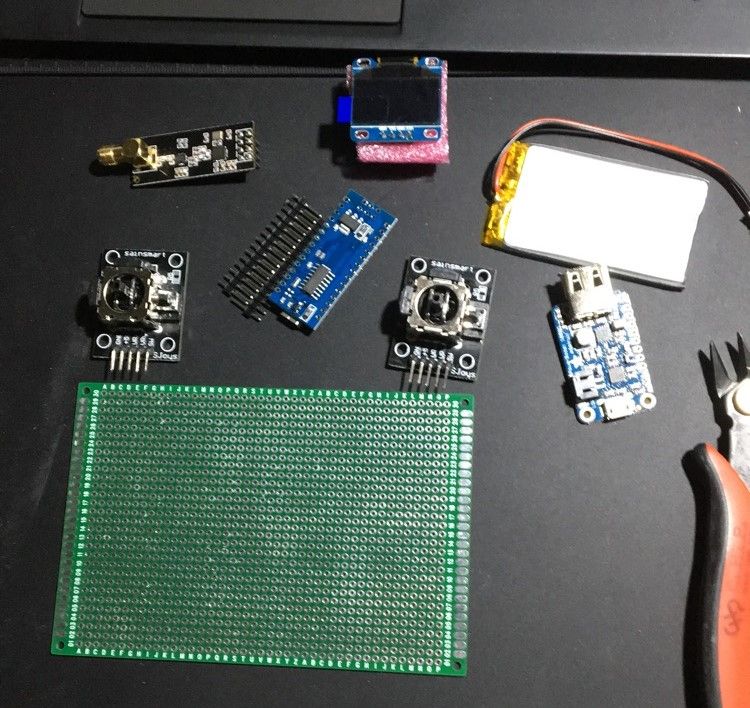
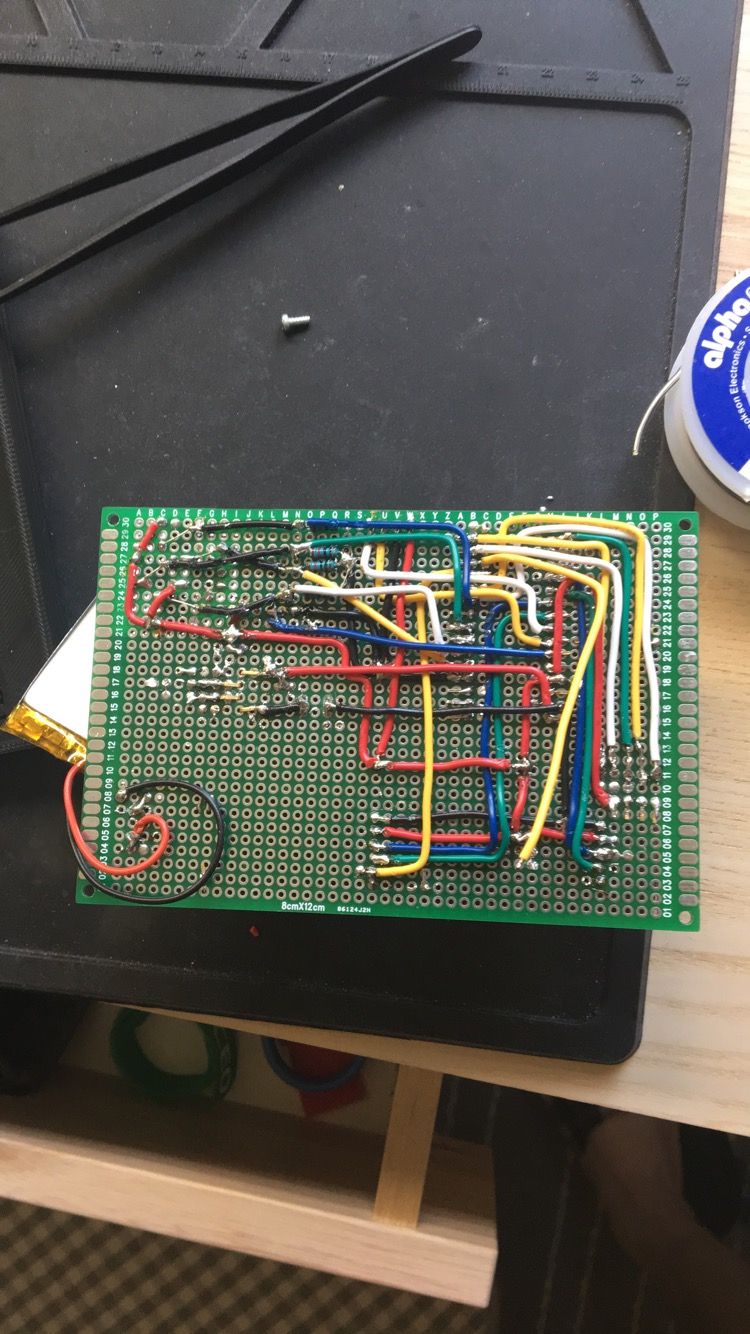
Controller Unit Components
- 1 x Arduino Nano,
- 1 x NRF24I01 radio modules,
- 1 x radio adapter(may come in bundle with the above link),
- 2 x Joystick,
- 1 x Charger module,
- 1 x Lithium Battery,
- 1 x OLED Display,
- N x tactile buttons or 5-way navigation buttons.
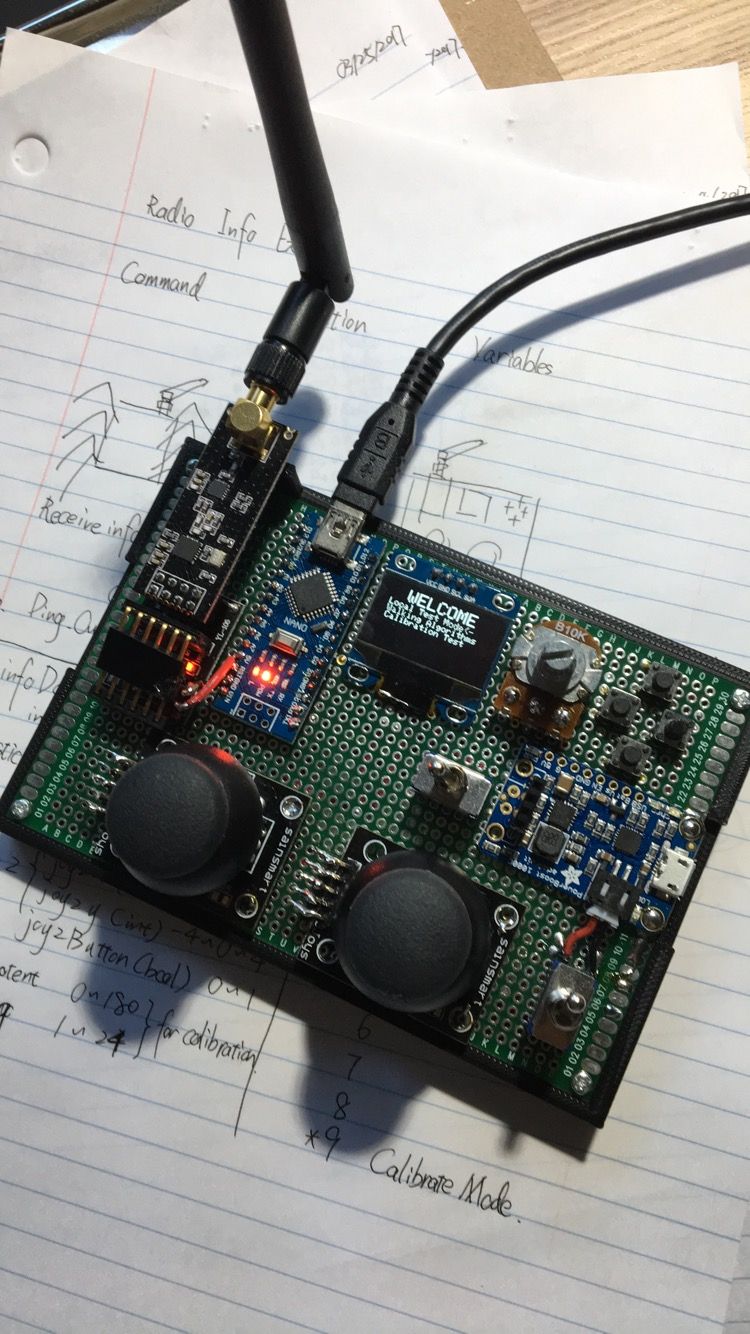
Controller GUI
A functional controller unit with a simple testing GUI. The battery is rechargeable through micro-USB.
Smooth Motion
Raw servo commands create jerky, robotic movement. To fix this, I implemented linear interpolation (lerp) that gradually transitions servos toward their target angles over multiple update cycles instead of jumping instantly. This creates the fluid, spider-like motion visible in the videos.
Controller Interface
The wireless controller features a menu-driven OLED interface with four operating modes: Local Test Mode, Walking Algorithms, Calibration Test, and Simultaneous Test. The display shows real-time connection status and uses a cursor-based navigation system. The controller continuously transmits joystick data via 2.4GHz radio while receiving acknowledgments from the robot, with timeout detection to indicate when connection is lost. A custom pixel-art spider logo displays on startup.

Circuit Design
Spidy LOGO
The startup screen is my customized Pixel Spider logo.
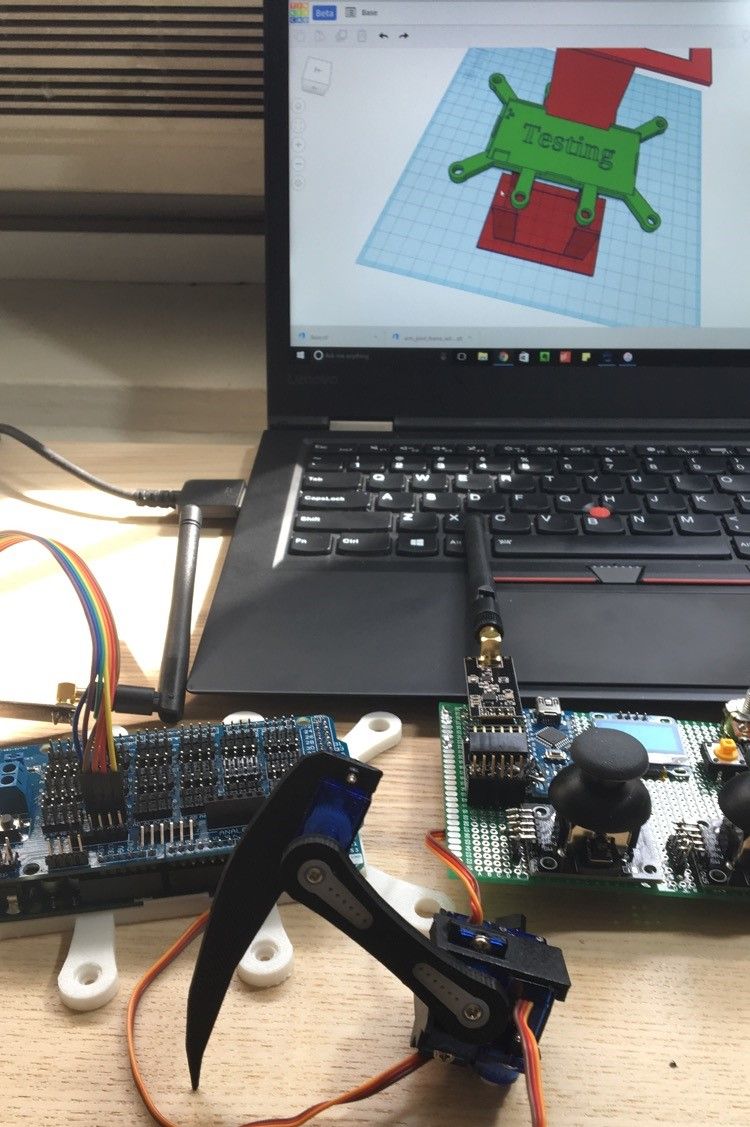
Body and Leg Design
An Arduino Mega with a servo shield, a completed controller without its case, and an assembled spider leg with 3 servo motors installed.
Completed Controller
A finished Controller with a solid 3D-printed case. The GUI indicates its wireless connection to Spidy and allows you to switch walking gait/algorithm and adjust individual motor base angle.
Servo Angle Correction
Individual motor correction from the radio controller.
Walking Algorithm Testing
Testing my walking algorithm in air.
Walking Speed Testing
Testing the maximum velocity of Spidy. Because the sharp tip of 8 legs don’t stick to the ground that well, I decided to design new touch-detecting leg with rubber tip.
Links
Code: https://github.com/jiatinglu99/Arduino-Spidy
CAD files:
https://www.tinkercad.com/things/btJxkIsPoQ8
https://www.tinkercad.com/things/kyyeG0oPm2c
https://www.tinkercad.com/things/3SHUKZcpVOv
https://www.tinkercad.com/things/9FsueHJEDek
New Leg Design
I designed new legs for Spidy with integrated touch sensors to detect ground contact. All 8 legs were fabricated and installed, though the sensor wiring and software integration remained as future work.
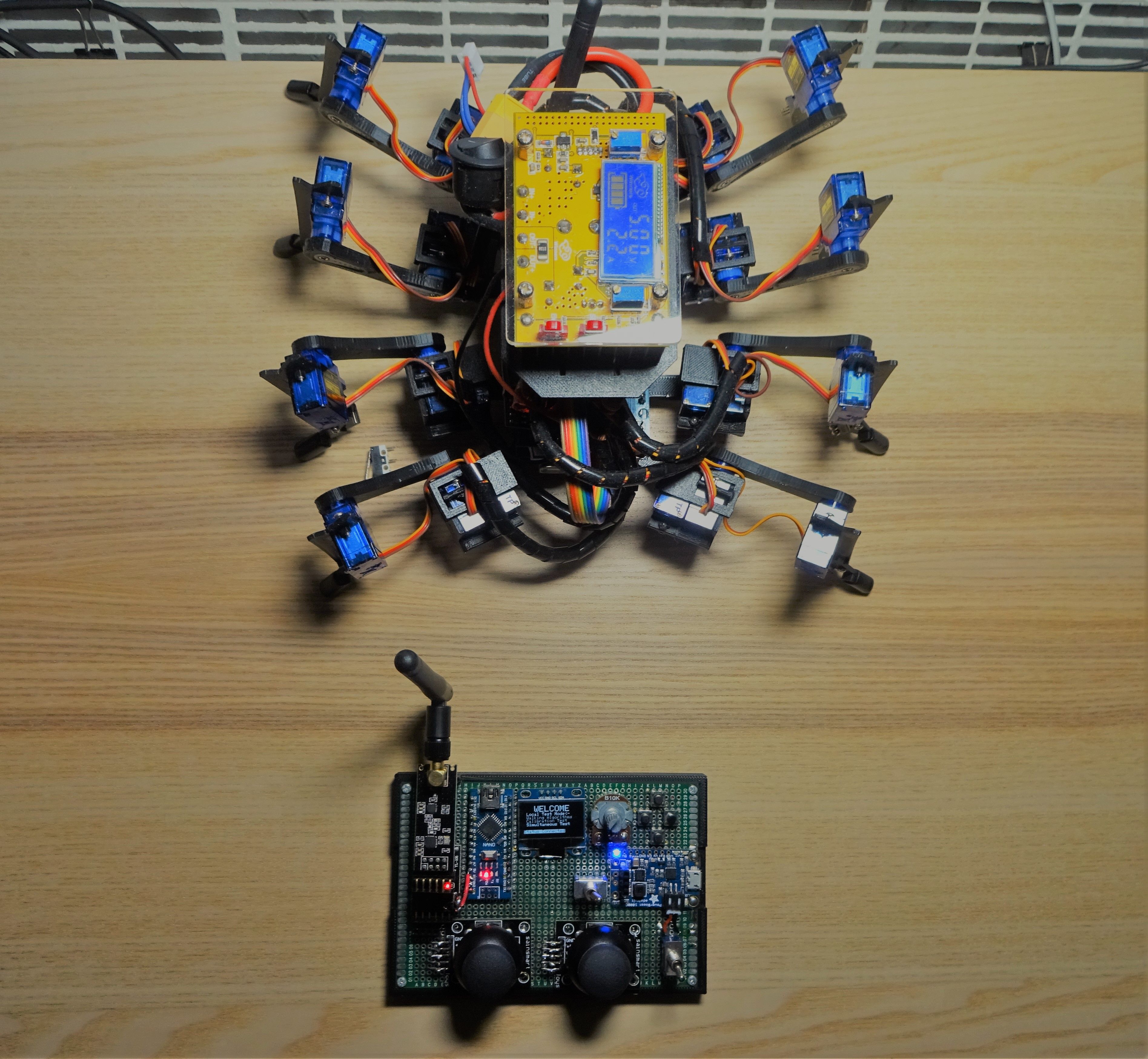
Booting…
A very satisfying moment when Spidy’s power is turned on and jumps into default resting gait.